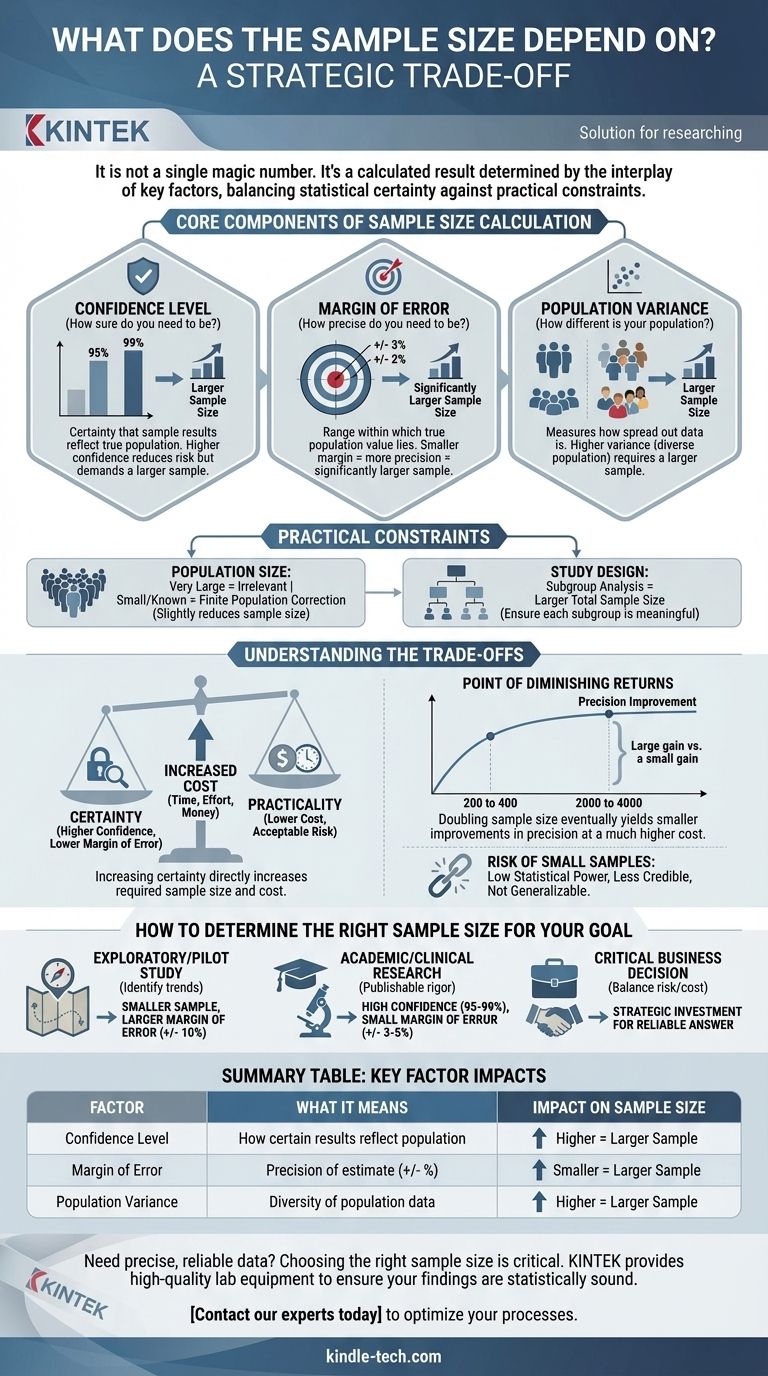
Para ser claro, o tamanho da sua amostra necessária não é um número mágico único. É um resultado calculado determinado pela interação entre o seu nível de precisão desejado, a sua tolerância ao risco e a variabilidade inerente da população que está a estudar. Os três fatores primários que deve definir são a sua margem de erro, o nível de confiança e a variância esperada da população.
A principal conclusão é que escolher um tamanho de amostra é uma troca estratégica. Está a equilibrar a necessidade de certeza estatística (precisão e confiança) com as restrições práticas dos seus recursos, como tempo e orçamento.

Os Componentes Essenciais do Cálculo do Tamanho da Amostra
Para determinar o tamanho da amostra apropriado, deve primeiro definir os parâmetros da sua pesquisa. Cada um dos seguintes componentes influencia diretamente o cálculo final.
Nível de Confiança (Quão certo precisa de estar?)
O nível de confiança indica o quão certo pode estar de que os resultados da sua amostra refletem a verdadeira população. É tipicamente expresso como uma percentagem, como 95% ou 99%.
Um nível de confiança de 95% significa que, se repetisse o estudo 100 vezes, esperaria que os resultados caíssem dentro do seu intervalo calculado em 95 dessas vezes.
Níveis de confiança mais altos reduzem o risco de estar errado, mas exigem um tamanho de amostra maior. Este é o preço que se paga por uma maior certeza nos seus resultados.
Margem de Erro (Quão preciso precisa de ser?)
A margem de erro define o intervalo dentro do qual espera que o verdadeiro valor da população se situe. É o valor "+/-" que frequentemente vê nos resultados de sondagens (por exemplo, "45% dos eleitores, com uma margem de erro de +/- 3%").
Uma margem de erro menor, como +/- 2%, indica uma estimativa mais precisa. No entanto, alcançar este nível mais elevado de precisão requer um tamanho de amostra significativamente maior.
Decidir sobre a sua margem de erro envolve pensar nas consequências de estar errado. Para decisões críticas, uma margem de erro menor é essencial.
Variância da População (Quão diferente é a sua população?)
A variância da população (ou desvio padrão) mede o quão dispersos os dados estão. Em termos simples, reflete o quão semelhantes ou diferentes os indivíduos na sua população são uns dos outros.
Se a sua população for muito uniforme (baixa variância), uma amostra menor pode representá-la com precisão. Se a sua população for altamente diversa, com opiniões ou características muito variadas (alta variância), precisa de uma amostra maior para capturar essa diversidade.
Como raramente se conhece a verdadeira variância de antemão, os estatísticos frequentemente usam uma estimativa conservadora (p=0.5) para garantir que a amostra seja suficientemente grande.
A Influência das Restrições Práticas
Além dos princípios estatísticos essenciais, fatores do mundo real também moldam o tamanho final da sua amostra.
Tamanho da População (Importa sempre?)
Para populações muito grandes (por exemplo, a população total de um país), o tamanho total torna-se irrelevante. A fórmula do tamanho da amostra estabiliza, e o número de que precisa não muda, quer a população seja de 1 milhão ou 100 milhões.
No entanto, se estiver a estudar uma população pequena e conhecida (por exemplo, todos os funcionários de uma empresa específica), pode aplicar uma Correção para População Finita. Isso pode reduzir ligeiramente o tamanho da amostra necessário.
Desenho e Complexidade do Estudo
A forma como desenha o seu estudo é importante. Se planeia analisar subgrupos dentro da sua amostra (por exemplo, comparar respostas de diferentes grupos etários), precisa de garantir que o tamanho da amostra para cada subgrupo seja suficientemente grande para ser significativo.
Isso muitas vezes significa que o tamanho total da amostra necessária deve ser maior do que se estivesse a olhar apenas para a população como um todo.
Compreender as Trocas
Escolher um tamanho de amostra é um exercício de gestão de prioridades concorrentes. Compreender as trocas inerentes é fundamental para tomar uma decisão informada.
O Custo da Certeza
Existe uma relação direta entre certeza e custo. Aumentar o seu nível de confiança e diminuir a sua margem de erro sempre aumentará o tamanho da amostra necessário, o que, por sua vez, aumenta o tempo, o esforço e o dinheiro necessários para o seu estudo.
O Risco de Amostras Pequenas
Usar uma amostra demasiado pequena é uma armadilha importante. Leva a uma baixa potência estatística, o que significa que pode não conseguir detetar um efeito ou diferença real que realmente existe.
Além disso, os resultados de amostras subdimensionadas são menos credíveis e podem não ser generalizáveis para a sua população, minando todo o propósito da pesquisa.
O Ponto de Retornos Decrescentes
É crucial reconhecer que existe um ponto de retornos decrescentes. Duplicar o tamanho da sua amostra de 200 para 400 pode reduzir significativamente a sua margem de erro. No entanto, duplicá-lo novamente de 2.000 para 4.000 produzirá uma melhoria muito menor na precisão, a um custo muito mais alto.
Como Determinar o Tamanho da Amostra Certo para o Seu Objetivo
A sua escolha deve ser guiada pelo objetivo específico da sua pesquisa.
- Se o seu foco principal for pesquisa exploratória ou um estudo piloto: Uma amostra menor com uma margem de erro maior (por exemplo, +/- 10%) é frequentemente aceitável para identificar tendências gerais e informar pesquisas futuras.
- Se o seu foco principal for pesquisa académica ou clínica: Deve priorizar o rigor com um alto nível de confiança (95% ou 99%) e uma pequena margem de erro (por exemplo, +/- 3-5%) para garantir que os seus resultados sejam robustos e publicáveis.
- Se o seu foco principal for uma decisão de negócio crítica: Deve equilibrar o custo da pesquisa com o risco financeiro de tomar uma decisão errada com base em dados imprecisos.
Em última análise, escolher o tamanho da amostra certo é sobre investir estrategicamente os seus recursos para obter a resposta mais confiável para a sua pergunta mais importante.
Tabela Resumo:
| Fator | O Que Significa | Impacto no Tamanho da Amostra |
|---|---|---|
| Nível de Confiança | Quão certo está de que os resultados refletem a população | Maior confiança = Amostra maior |
| Margem de Erro | A precisão da sua estimativa (por exemplo, +/- 3%) | Margem menor = Amostra maior |
| Variância da População | Quão diversa ou semelhante é a sua população | Maior variância = Amostra maior |
Precisa de dados precisos e confiáveis para a sua pesquisa ou controlo de qualidade?
Escolher o tamanho da amostra certo é fundamental para resultados válidos, quer esteja a realizar estudos académicos, pesquisa de mercado ou testes de materiais. Na KINTEK, entendemos que o sucesso do seu laboratório depende de dados precisos. Somos especializados no fornecimento de equipamentos e consumíveis de laboratório de alta qualidade de que precisa para executar a sua pesquisa sem falhas.
Deixe-nos ajudá-lo a otimizar os seus processos. Contacte os nossos especialistas hoje para discutir como as nossas soluções podem apoiar as suas necessidades específicas de laboratório e garantir que os seus resultados são estatisticamente sólidos.
Guia Visual
Produtos relacionados
- Moinho Vibratório de Laboratório
- Máquina Peneira Vibratória Tridimensional Úmida de Laboratório
- Peneiras de Teste de Laboratório e Máquina Vibratória de Peneira
- Moedor de Moinho de Moagem de Tecidos Micro Laboratoriais
- Moinho Vibratório de Disco Laboratorial para Moagem de Amostras
As pessoas também perguntam
- Qual papel um moinho de bolas centrífugo desempenha na ativação de resíduos de ligas à base de magnésio para produção de hidrogênio?
- Qual o papel de um moinho vibratório nas medições do potencial Zeta? Preparar Amostras Ultrafinas para Análise Precisa
- Qual é a função principal de um moinho de bolas vibratório de alta energia? Desbloqueie a Síntese Mecanocímica Avançada
- Qual é a função da moagem de bolas magnéticas de alta energia? Alcançar Refinamento em Nanoescala em Pós de Fe-Al
- Qual é o papel de um moinho de bolas vibratório de alta energia na preparação de YSZ-SiC? Alcançar Estruturas Perfeitas de Núcleo-Casca